
Calculating the break-even point in sales dollars will tell you how much revenue you need to generate before your business breaks even. As you can see, for the owner to have a profit of $1,200 per week or $62,400 per year, the company’s annual sales must triple. Presently the annual sales are $100,000 but the sales need to be $299,520 per year in order for the annual profit to be $62,400. As the result of its pricing, if Oil Change Co. services 10 cars its revenues (or sales) are $240. The latter is a similar calculation, but it’s based around knowing how much you bring in over a certain period of time.
How do you calculate your break-even point?
- Barbara is the managerial accountant in charge of a large furniture factory’s production lines and supply chains.
- The amounts and assumptions used in Oil Change Co. are also fictional.
- For example, If you sell both high-end electronics and low-cost accessories, a single break-even analysis won’t account for the differing profit margins.
- Upon doing so, the number of units sold cell changes to 5,000, and our net profit is equal to zero.
- Here are four ways businesses can benefit from break-even analysis.
The total variable costs will therefore be equal to the variable cost per unit of $10.00 multiplied by the number of units sold. In terms of its cost structure, the company has fixed costs (i.e., constant regardless of production volume) that amounts to $50k per year. Recall, fixed costs are independent of the sales volume for the given period, and include costs such as the monthly rent, the base employee salaries, and insurance. Break-even analysis can help determine those answers before you make any big decisions.
You’re our first priority.Every time.
In other words, it is used to assess at what point a project will become profitable by equating the total revenue with the total expense. Another very important aspect that needs to address is whether the products under consideration will be successful in the market. Therefore, ABC Ltd has to manufacture and sell 100,000 widgets in order to cover its total expense, which consists of both fixed and variable costs. At this level of sales, ABC Ltd will not make any profit but will just break even. For options trading, the breakeven point is the market price that an underlying asset must reach for an option buyer to avoid a loss if they exercise the option.
Move, manage, and grow your money
Now we can take that concept and translate it into sales dollars. The variable costsclosevariable costsVariable costs are expenses a business has to pay which change directly with output, eg raw materials. Break-even analysis works well for short-term planning, like setting business formation what are some of the advantages or disadvantages of a sole proprietorship immediate sales goals or dedication to prices. Let’s say you run a small bakery and plan to expand the bakery by opening a second location next year. Your break-even analysis alone won’t factor in the increased rent, higher utility bills, or additional staff wages.
What is an example of a break-even point calculation?
Variable costs are incurred only when a sale is made, meaning you only pay for what you need. Outsourcing these nonessential costs will lower your profit margin and require you to sell fewer products to make a profit. Break-even analysis can also be a great way to measure and benchmark your business’s performance over time. Over the past couple of months, you’ve consistently sold 400 units, meaning you’re exceeding your goal and generating profit. On the other hand, if you’re only selling 250 units, you’ll need to either increase sales or lower costs to hit that target. Tracking this data over time can help you identify patterns — e.g., slower sales during specific months — so you can adjust your strategy based on those trends.
Reduce variable costs
The incremental revenue beyond the break-even point (BEP) contributes toward the accumulation of more profits for the company. If a company has reached its break-even point, the company is operating at neither a net loss nor a net gain (i.e. “broken even”). Businesses share the similar core objective of eventually becoming profitable in order to continue operating. Otherwise, the business will need to wind-down since the current business model is not sustainable.
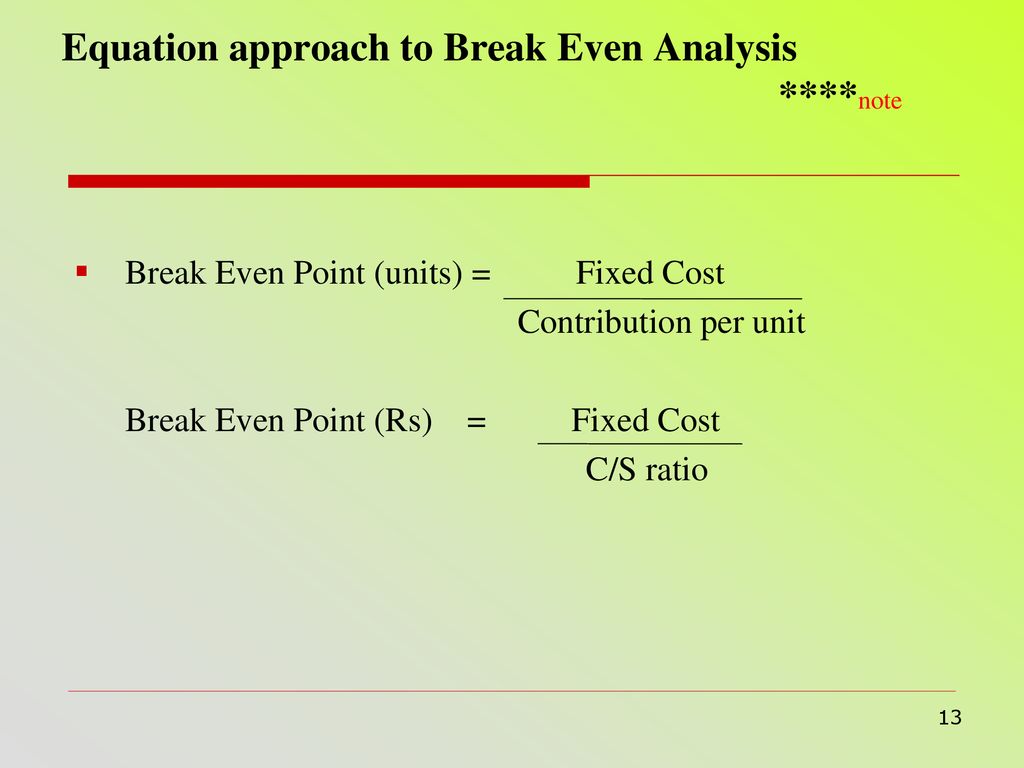
Dividing the fixed costs by the contribution margin will reveal how many units are needed to break even. Break-even analysis, or the comparison of sales to fixed costs, is a tool used by businesses and stock and option traders. It is essential in determining the minimum sales volume required to cover total costs and break even.
Managers utilize the margin of safety to know how much sales can decrease before the company or project becomes unprofitable. As we can see from the sensitivity table, the company operates at a loss until it begins to sell products in quantities in excess of 5k. For instance, if the company sells 5.5k products, its net profit is $5k. Bond investors routinely have to make judgment calls about expectations on future conditions in the credit markets, including changes in prevailing interest rates and inflation. Using a break-even calculation can help assist investors in making those judgment calls in a more informed way.
Let’s take a look at a few of them as well as an example of how to calculate break-even point. The formula for break-even point (BEP) is very simple and calculation for the same is done by dividing the total fixed costs of production by the contribution margin per unit of product manufactured. If the company can increase its contribution margin per unit to $8 (by perhaps lowering its per unit variable cost), it only needs to sell 8,750 ($70,000 / $8) to break even. Break-even analysis compares income from sales to the fixed costs of doing business. The five components of break-even analysis are fixed costs, variable costs, revenue, contribution margin, and break-even point (BEP). When you outsource fixed costs, these costs are turned into variable costs.
He is considering introducing a new soft drink, called Sam’s Silly Soda. He wants to know what kind of impact this new drink will have on the company’s finances. So, he decides to calculate the break-even point, so that he and his management team can determine whether this new product will be worth the investment. The break-even point allows a company to know when it, or one of its products, will start to be profitable. If a business’s revenue is below the break-even point, then the company is operating at a loss.

